1. About Python classes and objects
Haven't you thought that you used and still use OOP all the time without realizing it?
Even using other paradigms in Python, you still use objects to do almost everything.
This is because, in Python, everything is an object.
Remember the definition of an object: An object in Python is a unique collection of data (attributes) and behaviors (methods).
This matches any data type in Python.
Let's take a simple example: a simple character string is an object which has properties (attributes) and methods (upper(), lower(), center(), count() etc…). As you see in the figure below:
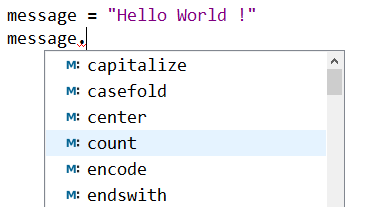
The same goes for integers, floats, booleans, lists and dictionaries etc.
In general, a class in OOP is a code model from which we create what are called objects (we also say instances or instance objects)
2. Classes in Python
To create a class in Python, we use the instruction:
class name_of_the_class
We then create a method that allows us to build the objects, called constructor via the instruction:
# define the class constructor
def __init__(self):
...
Example. Person class
class Person:
# define the class constructor
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name = name # define the name attribute
self.age = age # define the age attribute
# creating of an instance object
P = Person("Albert",27)
# display instance attributes
print("The person's name is: ", P.name)
print("The person's age is: " , P.age, " years")
"""
output:
The person's name is: 'Albert'
The person's age is: '27 years'
"""
Example. Rectangle class
class Rectangle:
# define the class constructor
def __init__(self,L,l):
self.Length=L # define the Length attribute
self.Width=l # define the Width attribute
# creating of an instance object
myRectangle=Rectangle(7,5)
# display the the instance attributes
print("The length of my rectangle is: ",myRectangle.Length)
print("The width of my rectangle is: ",myRectangle.Width)
"""
output:
The length of my rectangle is: 7
The width of my rectangle is: 5
"""
3. Instance methods in Python
Definition An instance method is any named method or procedure within the class, allowing to define properties or behaviors of instance objects. An instance method has one or more parameters, the first parmeter must be named self!
Example. adding an instance method that calculates the area of the rectangle
class Rectangle:
def __init__(self,L,l):
self.Length=L
self.Width=l
# instance method that calculates area
def area(self):
return self.Length*self.Width
# create a rectangle of length 7 and width 5
myRectangle = Rectangle(7.5)
print("The area of my rectangle is: ", myRectangle.area())
# output: The area of my rectangle is: 35
4. Class methods in Python
A class method in Python is a method that works within the class where it was created and it is accessible by an instance object or directly by using the class name without doing any instantiation! A class method is characterized by:
- It works inside the class where it was and is accessible through an object instance or using the class name!
- A class method is decorated by @classmethod
- A class method has a mandatory first parameter named cls
5. Instance attributes and class attributes
An instance attribute is an attribute that works with an instance object while a class attribute is an attribute that works with the class
Example 1. instance attributes & class attributes
class Student:
name = 'Aladdin' # class attribute
def __init__(self):
self.age = 30 # instance attribute
@classmethod
def displayName(cls):
print("Student name is:", cls.name)
# we can use the class method without doing any instantiation !
print(Student.displayName())# output: Student name is: Aladdin
# the class method can also used by an instance object
Stud = Student()
print(Stud.displayName())# output: Student name is: Aladdin
6. Static methods
Static methods, work like class methods, are methods that are bound to a class rather than its object.
statics methods can be executed without going through instantiation
Example. static method
class myClass:
def __init__(self):
pass
# create a static method
@staticmethod
def myStaticMethod():
print("Here is an example of a static method in Python")
myClass.myStaticMethod()
# output: 'Here is an example of a static method in Python'
Younes Derfoufi
my-courses.net